Houcai Guo

Houcai Guo's personal homepage.
Biography
My name is Houcai Guo. I received the M.Sc. degree in Remote Sensing of Geographical Environment from the School of Geography, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, in June 2023. I am currently a PhD student at the Remote Sensing Laboratory, University of Trento, Italy.
My current research interests include the spatiotemporal fusion, registration, and time-series analysis of remote sensing images.
I am a Graduate Student Member of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society, IEEE.
External Links
E-mail
Google Scholar
ResearchGate
ORCID
Visitors
Selected Pulications
[1] H. Guo, D. Ye, H. Xu, and L. Bruzzone, “OBSUM: An object-based spatial unmixing model for spatiotemporal fusion of remote sensing images,” *Remote Sensing of Environment, vol. 304, p. 114046, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2024.114046.
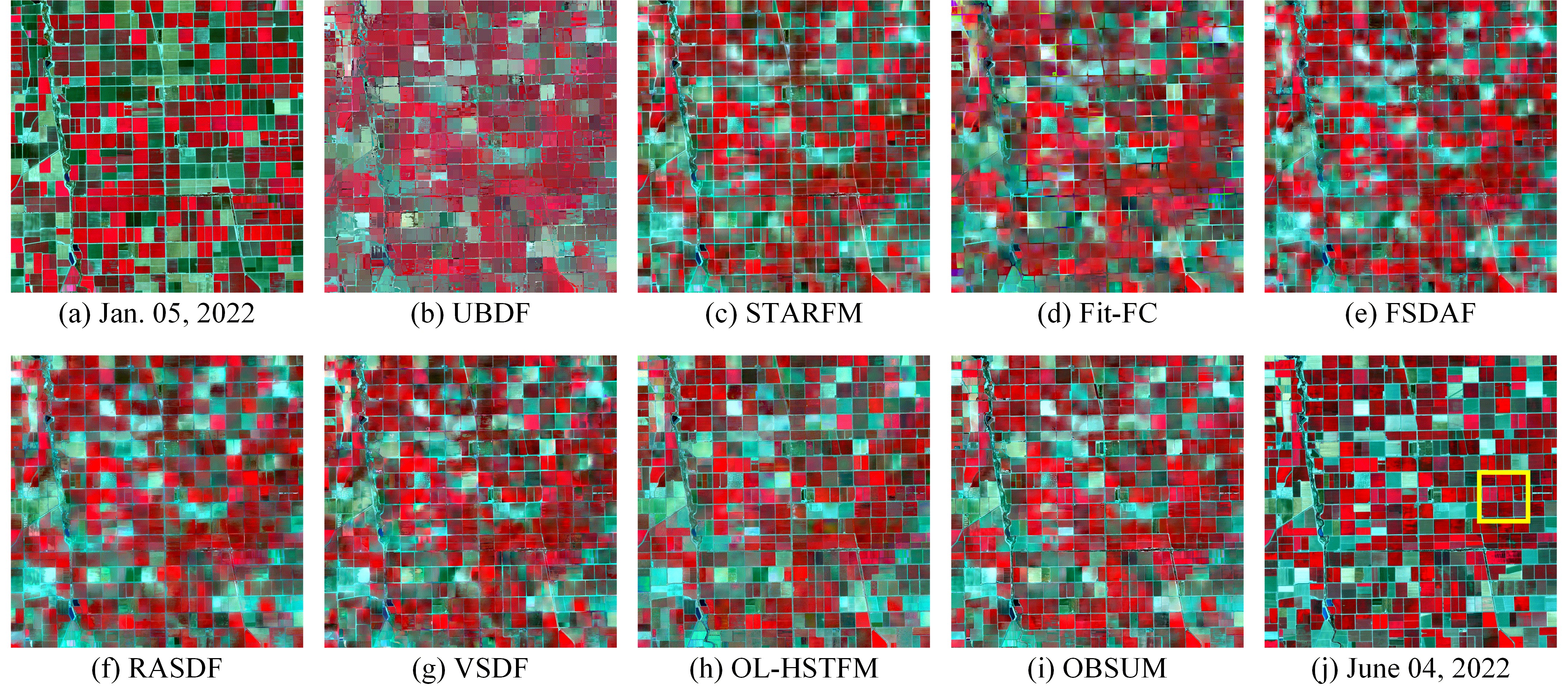
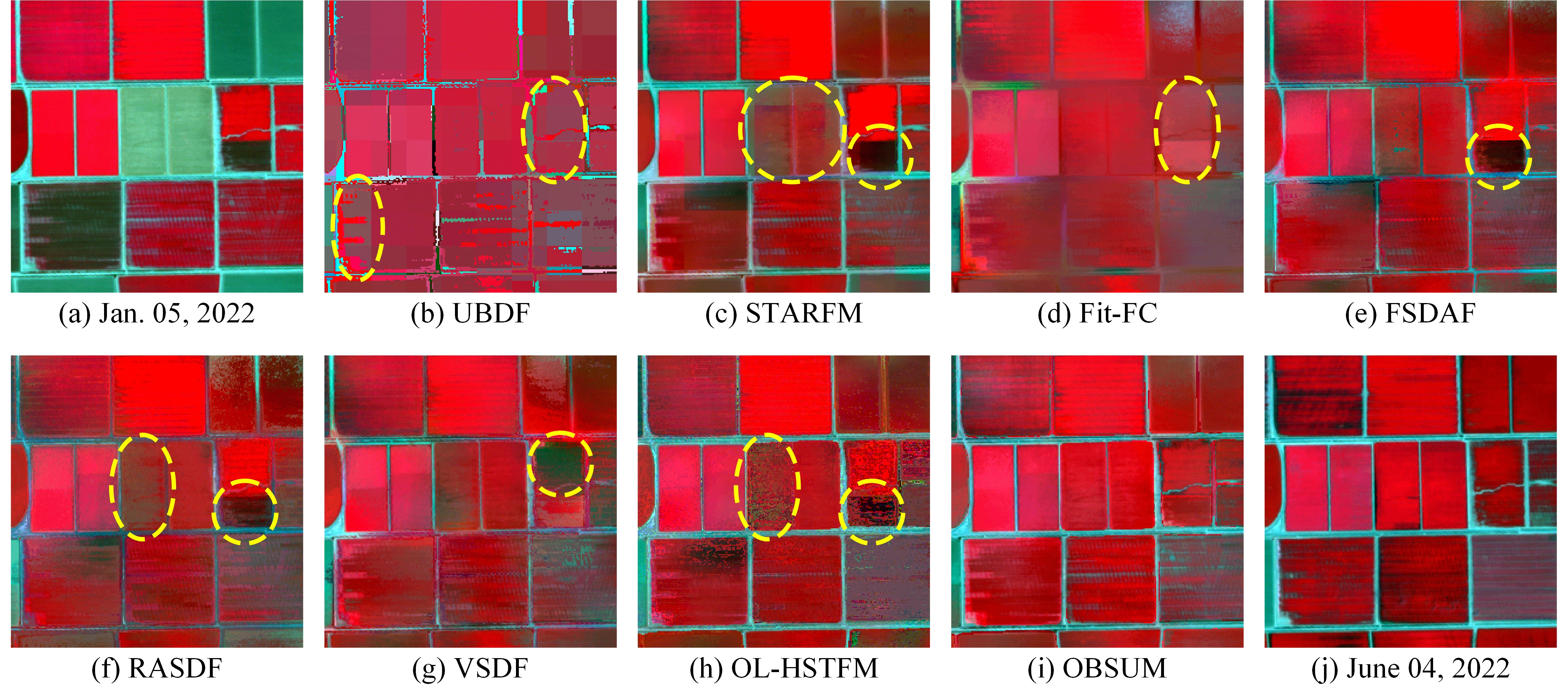
We propose an Object-Based Spatial Unmixing Model (OBSUM) to fuse images with different spatial and temporal resolutions. OBSUM is a hybrid method that utilizes object-level shape information to obtain more accurate fusion results. The experimental results demonstrate that OBSUM can retrieve both strong phenological changes and land-cover changes, thus outperforming the comparison methods in terms of visual effect and four accuracy indices. Benefiting from its accurate fusion performance, OBSUM has great potential for supporting various remote sensing applications at a fine spatial scale, such as dynamic crop progress monitoring and crop mapping.
[2] H. Guo, H. Xu, Y. Wei, Y. Shen, and X. Rui, “Outlier Removal and Feature Point Pairs Optimization for Piecewise Linear Transformation in the Co-registration of Very High-resolution Optical Remote Sensing Imagery,” *ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, vol. 193, pp. 299-313, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.09.008.
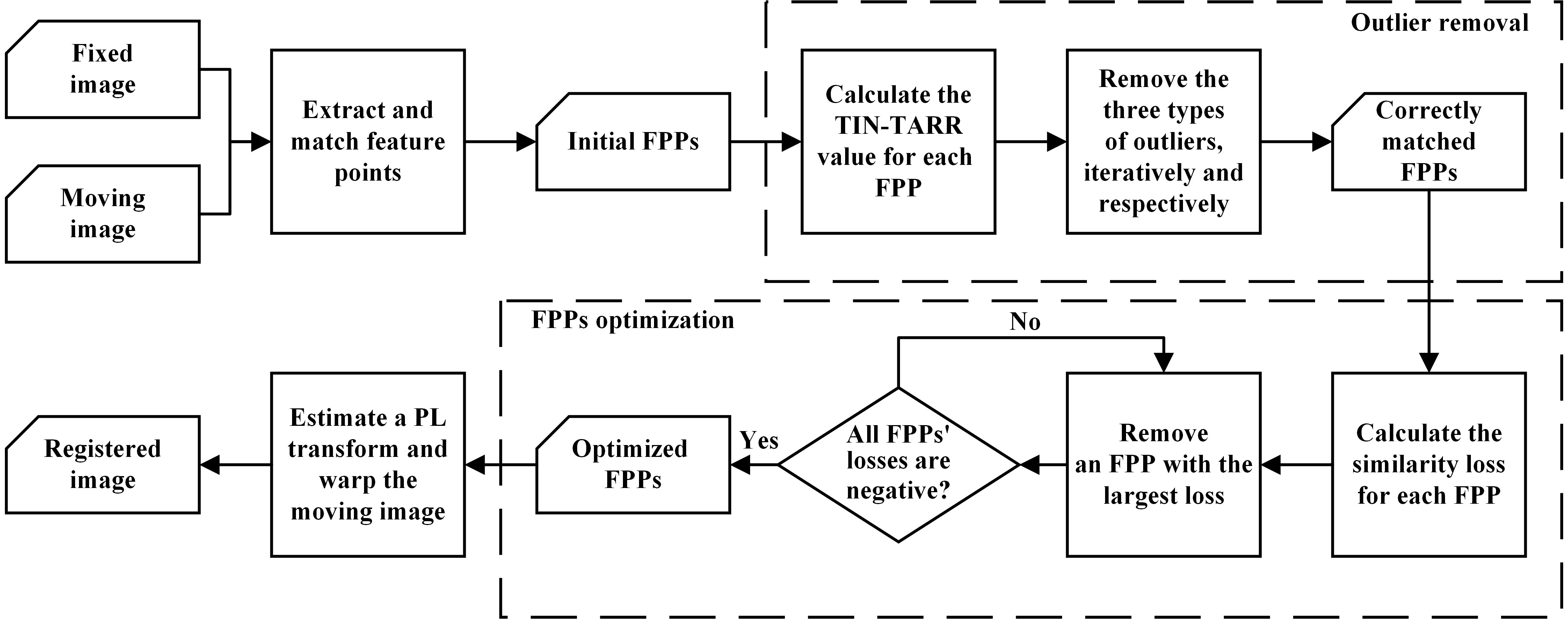
The piecewise linear (PL) transformation has been widely applied to handle the local deformations between very high-resolution remote sensing images. However, PL transformation is very sensitive to the mis-matched points, i.e., the outliers. In this paper, we first proposed an outlier removal method that considers the intrinsic characteristic of the PL transformation. After that, the feature points were optimized by maximizing the similarity between the fixed and the registered images to further improve the registration accuracy of the PL transformation.
[3] H. Guo, H. Xu, Y. Wei, and Y. Shen, “Point Pairs Optimization for Piecewise Linear Transformation of Multimodal Remote Sensing Images by the Similarity of Log-Gabor Features,” *IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, vol. 19, pp. 1-5, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2022.3207592.
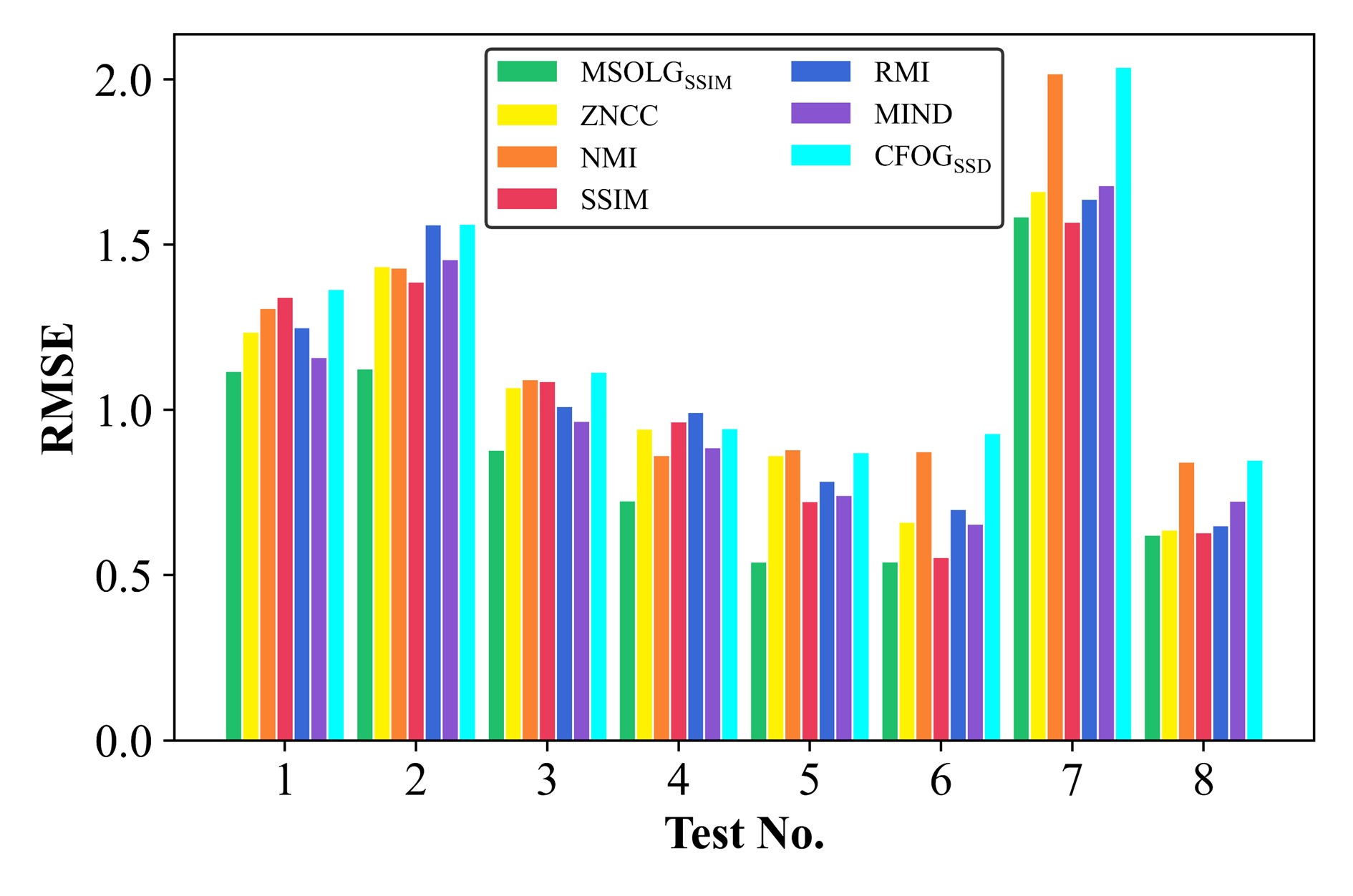
Aiming to optimize the feature points in the piecewise linear registration of multimodal remote sensing images, we proposed a novel similarity metric that combines the Log-Gabor features with structural similarity. The proposed similarity metric outperformed six other commonly-used and state-of-the-art similarity measurements.